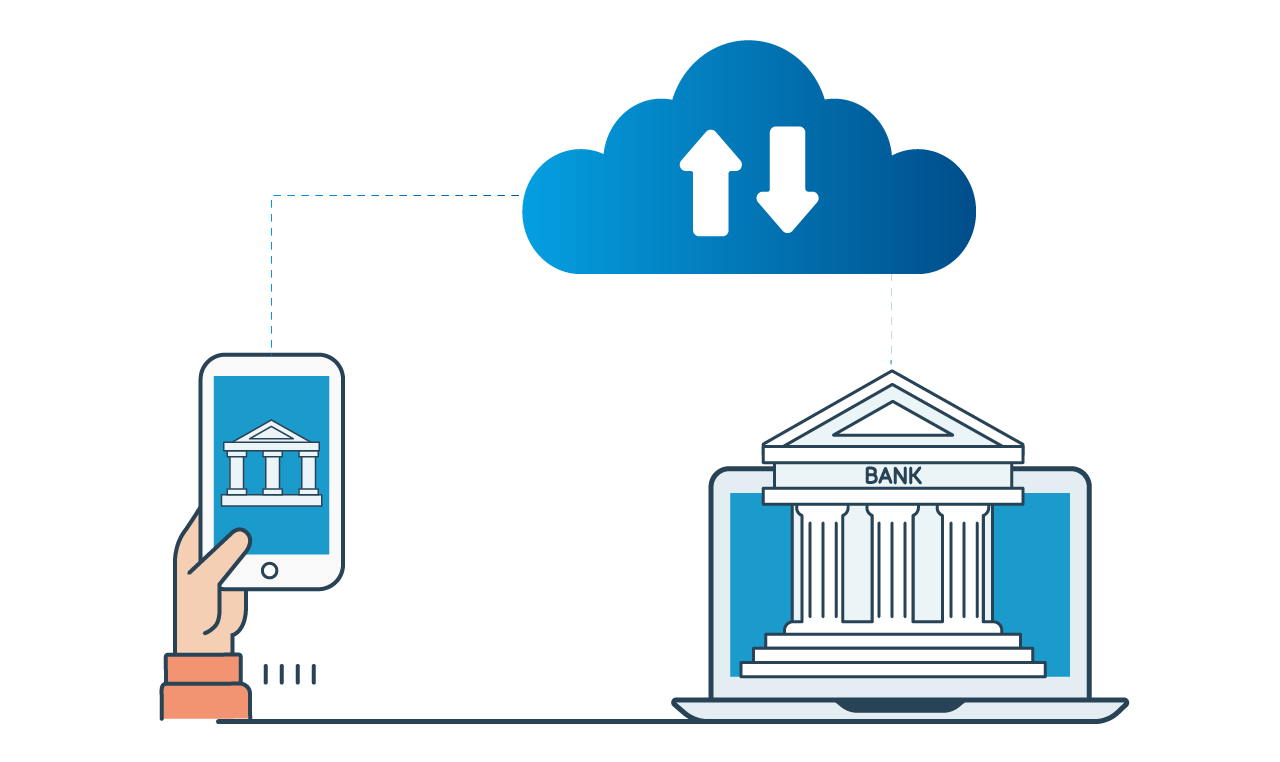
Banks are facing a growing need to plan for the future due to changing consumer expectations, new business models, and emerging technologies. One clear indicator of this shift is the increasing adoption of cloud computing in banking. As a result, cloud has become a focal point of interest for C-suite executives and board members, with banking leaders increasingly recognizing its importance for data storage and applications.
As cloud usage continues to rise, top public-cloud service providers are now offering ‘products-as-a-service’ to help banks generate revenue, control costs, gain better customer insights, and deliver market-relevant products and services. In addition, cloud computing can aid in the monetization of enterprise data assets.
Cloud also provides opportunities for enterprise synchronization, enabling banks to break down data and operational silos across finance, customer support, risk management, and other departments. By accumulating massive data sets in one place, organizations can apply analytics to gain cross-functional insights.
When businesses choose to transition from their legacy systems to cloud computing, there are various types of cloud computing that they can adopt. The gradual approach of increasing cloud adoption is a popular strategy, and mixing and matching different hybrid models to suit business needs can be a wise decision.
Cloud computing has various applications in the banking industry, including:
- Fraud detection and prevention: This is one of the primary applications of cloud computing. By analyzing large amounts of data from various sources, banks can detect suspicious activities before they become a threat to the organization.
- Data analysis: Cloud computing enables banks to use advanced analytics to discover customer patterns and preferences. This information can be used to create better offers and products that meet their customers’ needs.
- Cloud-based customer relationship management (CRM): This allows banks to process customer interactions and data regardless of time or location. With cloud-based CRM, banks can offer personalized solutions to their customers more easily.
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the banking industry. Prior to 2020, there was already a need for banks to upgrade their customer service for the digital age. However, the pandemic has made this a necessity.
If the customer experience is inadequate, customers may choose to take their business elsewhere. To address this challenge, banks have become proactive about their use of data-efficient, cloud-based services. Many banks have already taken measures to incorporate cloud technology extensively into their business and operations models.
Potential Risks of Delaying Cloud Integration
Despite the numerous benefits of cloud technology, many financial institutions still hesitate to embrace it due to various reasons. However, delaying the integration of cloud computing can pose significant risks for banks.
Replacing existing systems and transitioning from legacy technology can be complex and risky. Furthermore, there may have been concerns about the security of cloud computing in the past. However, cloud technology has evolved significantly in recent years and is now considered a reliable and secure option for data storage.
One of the main challenges in adopting new technology is the organizational changes that come with it. Banks, as highly-regulated and complex organizations, need to plan and execute this transition carefully.
On the other hand, delaying the adoption of cloud technology can give competitors an opportunity to upgrade and gain an edge in terms of customer experience. Hence, it is important for banks to consider the potential risks of delaying the shift to cloud and take proactive measures to integrate it into their operations.
In conclusion, cloud computing has become an essential tool for banks to remain competitive in the digital age, but the path to adoption comes with challenges and obstacles. It is crucial for financial institutions to implement robust risk management strategies to detect and address potential threats effectively.
However, these adoption challenges can be overcome by ensuring that the organization’s IT infrastructure complies with rigorous project management, security, and data protection protocols.
Thank you for reading. For continued insights and in-depth discussions, please follow our blogs at Ezeiatech.